Understanding Alopecia
“Alopecia” is simply a medical umbrella term for hair loss. It is a complex issue that can be triggered by external factors, such as harsh hair care practices, or internal issues like autoimmune diseases or thyroid disorders. Generally, hair loss is categorized into two main types: non-scarring and scarring. Identifying which category you fall into is the first step toward effective treatment.

Common Types of Hair Loss
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as pattern hair loss, this is largely genetic. In men, it often starts at the temples or the crown. In women, it typically manifests as a widening of the midline part or thinning at the crown.
- Telogen Effluvium: This is excessive shedding across the entire scalp. It often occurs after significant physical or psychological stress, such as systemic illness or hormonal changes post-pregnancy.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own hair follicles, usually resulting in small, round patches of hair loss on the scalp or body.
- Traction Alopecia: Common in those who wear tight hairstyles like braids or ponytails. While it starts as non-scarring, it can become permanent if the tension continues.
- CCCA (Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia): A progressive type of scarring hair loss that often starts at the crown and expands outward. It requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent scarring.

Expert Tips for Prevention and Regrowth
1. See a Dermatologist Early
Early diagnosis is the single most important factor in successfully treating hair loss. The sooner you see a board-certified dermatologist, the more likely you are to respond to treatment before the loss becomes permanent.
2. Prepare for Your Appointment
To get the most out of your visit, keep a detailed record of your symptoms:
- Note any itching, pain, or tenderness.
- Document your family medical history and any recent illnesses.
- Bring a list of all medications and supplements you are currently taking.
- Be ready for a potential scalp biopsy or blood work to check for nutritional deficiencies.
3. Practice Responsible Styling
Stop any styling practices that put excessive tension on your scalp. Avoid tight braids, heavy extensions, or constant high ponytails. If you experience pain or small bumps around your hair follicles while getting your hair styled, it is a clear sign that your follicles are under attack.
4. Consider Evidence-Based Treatments
While you should always consult a physician before starting new treatments, several options have clinical evidence for supporting hair regrowth:
- Supplements: Vitamin D, Zinc, and specialized hair supplements can support inflammatory or autoimmune states.
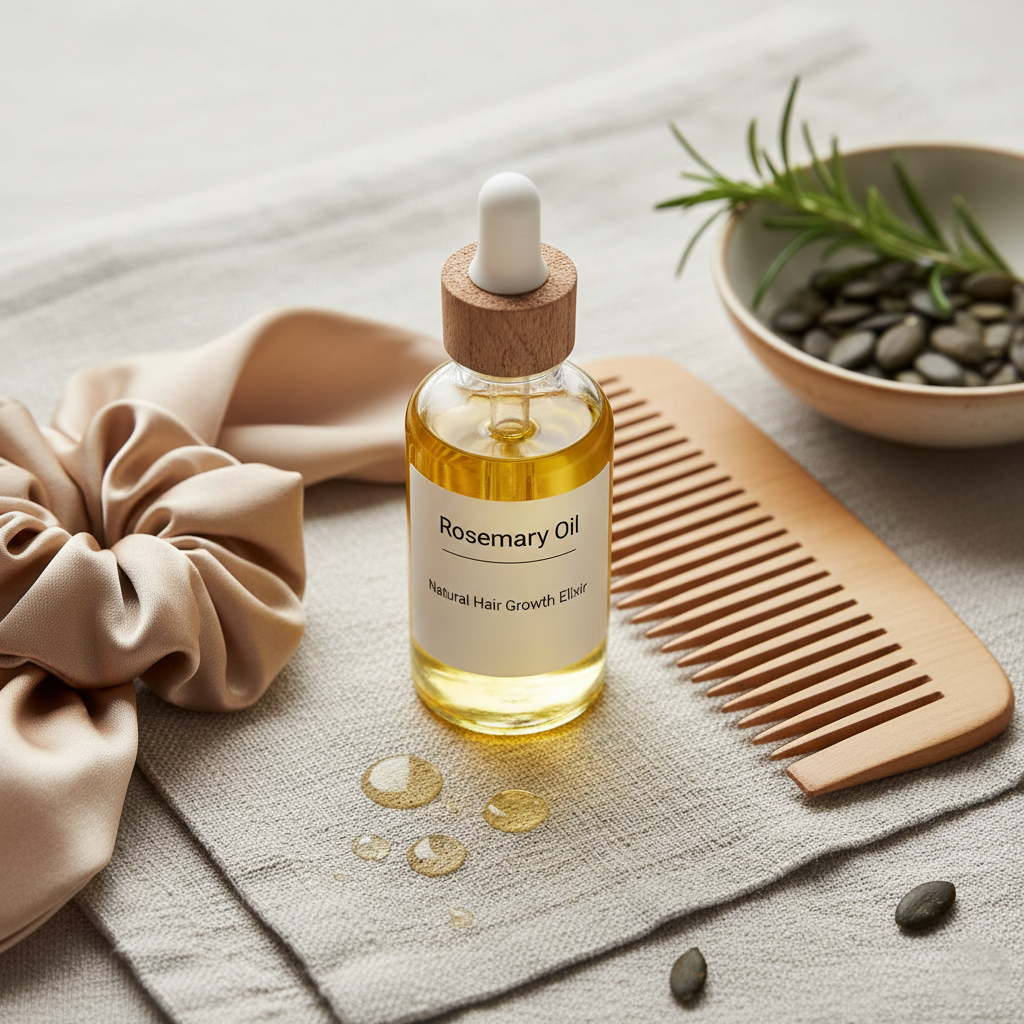
- Topicals: Minoxidil is a common medical treatment, while natural options like rosemary oil or pumpkin seed oil also show promise.
- Light Therapy: Low-level photomodulation (hair combs or helmets) can be effective for certain types of thinning.
5. Manage Stress Levels
Stress can both cause and worsen hair loss, creating a frustrating cycle. Finding healthy ways to reduce stress is not just good for your mental well-being; it is a vital part of your hair regrowth strategy.
By taking proactive steps and seeking professional guid













Leave a comment