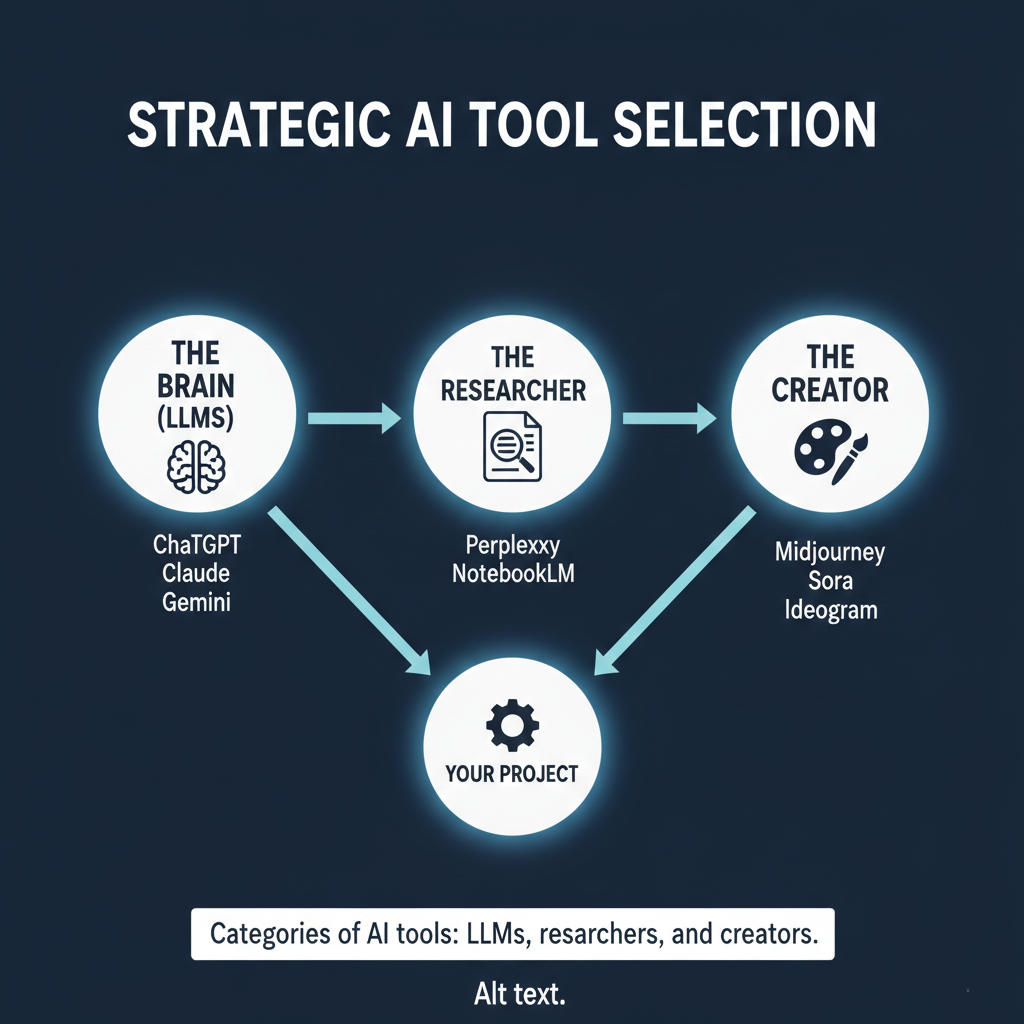
Skill 1: Strategic Tool Selection
A beginner tries to use one AI tool for everything. A pro knows that different tools excel at different tasks. Think of it as building a specialized team. You wouldn’t hire one person to handle design, accounting, and engineering; similarly, you should master a small set of tools categorized into three groups:
- The Brain (LLMs): Use ChatGPT for everyday versatile tasks, Gemini for document analysis and web integration, and Claude for human-sounding writing and coding.
- The Researchers: Use Perplexity for fact-checking with verified sources and NotebookLM for summarizing and connecting information across your own uploaded materials.
- The Creators: Use specialized tools like Midjourney or Google’s image models for visuals, and tools like Ideogram for graphics and diagrams.
Skill 2: Problem Clarification
Beginners jump straight into prompting with a vague idea, which leads to vague results. Pros spend time clarifying the problem before opening an AI tool. If you ask for “food” at a restaurant, you get whatever the waiter brings. If you specify you want a spicy vegetarian meal in 30 minutes, you get exactly what you need. Before prompting, define your goal, your audience, and what success looks like.
Skill 3: Effective AI Communication
How you communicate with AI determines the quality of the output. Four techniques can transform your results:
- The Six-Part Framework: Provide Role, Context, Task, Format, Rules, and Examples. Pro tip: put the most important information at the end of the prompt for stronger influence.
- Show, Don’t Just Tell: Upload screenshots, PDFs, or examples of styles you love. Showing a landing page design you admire is much more effective than describing it with text.
- Meta-Prompting: Ask the AI to act as a prompt engineering expert to help you build or improve your prompts.
- Self-Critique: Force the AI to critique its own work, identify weaknesses, and provide a revised version.
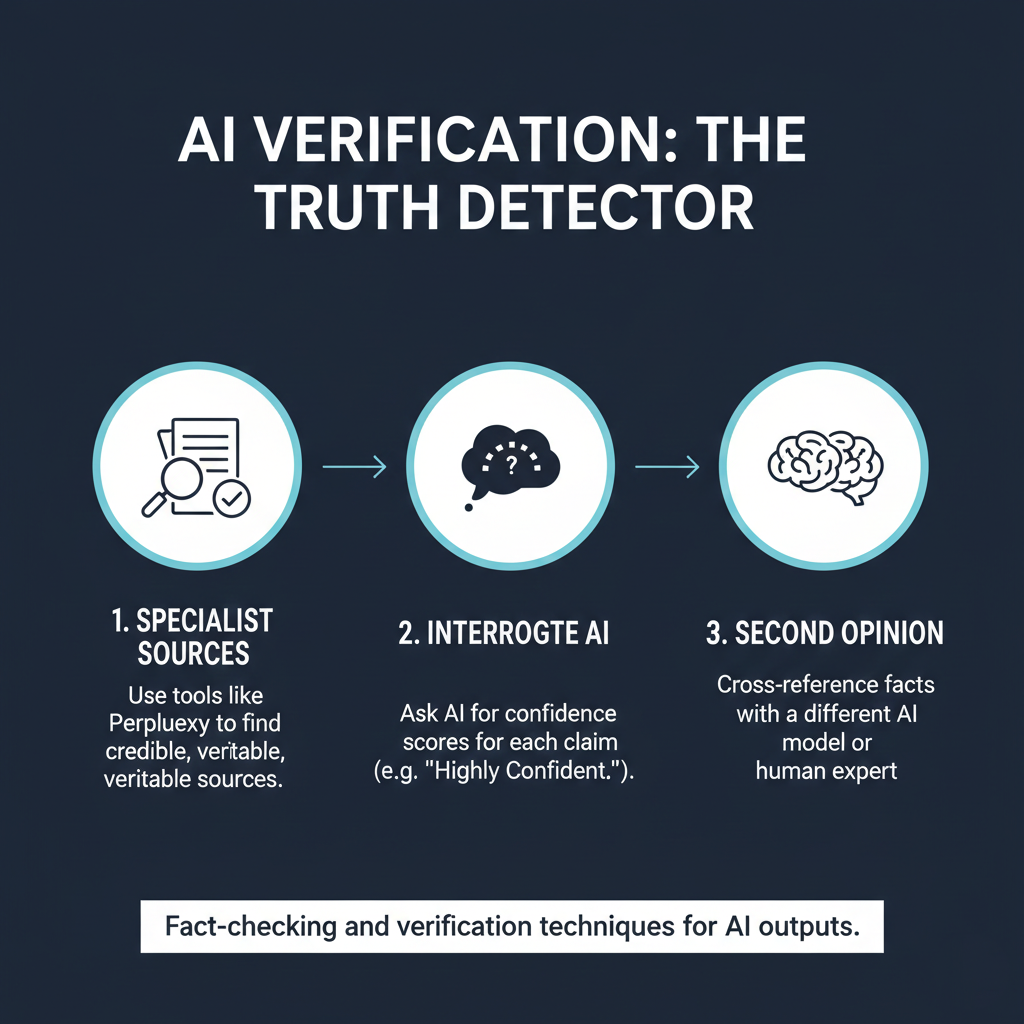
Skill 4: Verification (The Truth Detector)
AI can be a confident liar, often making things up through “hallucinations.” Never blindly trust the output. Instead:
- Fact-check with a specialist: Take statistics to Perplexity and ask for the specific source link.
- Interrogate the AI: Ask it to rate its confidence level for each claim (e.g., “Highly confident” vs. “Speculative”).
- Get a second opinion: Paste the output into a different AI model (like Claude) and ask it to find errors or logical gaps.
Skill 5: Workflow Orchestration
Real power comes from combining tools, either manually or through automation.
- Manual (Tool Stacking): Use different tools in a sequence for a unique project—for example, research stats in Perplexity, write copy in ChatGPT, and generate a graphic in Ideogram.
- Automated (AI Agents): For repetitive, predictable workflows, use AI agents that autonomously plan and execute tasks, such as drafting quotes based on form submissions.
Skill 6: The Human Polish
The final 20% is what makes content actually connect with people. AI-generated content often sounds generic and “corporate.” To make it resonate, you must add:
- Vision: Inject your unique voice and personal stories.
- Taste: Trim the “AISMs”—the predictable corporate jargon that AI loves to use.
- Care: Add a human connection that shows you understand your audience’s frustrations and needs.
Mastering AI isn’t about memorizing a list of prompts; it’s about mastering the process. The AI is the doer, but you are the director. By focusing on these six skills, you can close the gap and start achieving professional-level results in your work and life.














Leave a comment